
json解析器差异导致的安全问题
前段时间在准备技术分享内容,看到JSON Interoperability类型的漏洞,感觉还挺有意思,整理一些案例和工具分享下
1.背景
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写,同时也易 于机器解析和生成。它基于JavaScript语言标准ECMA-262第3版(1999年12月)的一个子集。随着时间的推移,JSON已经超越了JavaScript,成为许多编程语言支持的标准数据格式之一。
如HTTP 请求走私等攻击一样,json解析器之间以及多阶段请求处理的差异可能引入严重的漏洞,即使是在严格遵守规范的解析器,也不可避免的与规范存在偏差,这是为什么?
1.关于JSON的规范有多个,各规范定义有一定的差异
- ECMAScript Standard:ECMAScript是JavaScript语言的标准化名称,定义了JSON作为JavaScript的一个子集,但实际应用超出了JavaScript
- IETF JSON RFC 8259:提供了一个严格和精确的JSON数据交换格式规范,这个标准旨在确保JSON数据的交换在不同的系统间能够保持一致性和可靠性
- ……
2.规范文档对于一些定义是开放式的描述,例如 IETF JSON RFC 8259 对重复键的描述
An object whose names are all unique is interoperable in the sense that all software implementations receiving that object will agree on the name-value mappings. When the names within an object are not unique, the behavior of software that receives such an object is unpredictable. Many implementations report the last name/value pair only. Other implementations report an error or fail to parse the object, and some implementations report all of the name/value pairs, including duplicates.
只是说明了各种解析器对重复键值处理的各种现象,并没有规定当重复键出现时应怎么处理。
那么主要有哪些JSON解析差异可能会导致漏洞?
- 重复键的优先级差异。
- 特殊键解析差异:字符截断和注释
- JSON序列化结构差异
- 浮点数和整数表示差异
- 解析容错机制和其他bug
- ……
更多的差异分类和细节可参考https://bishopfox.com/blog/json-interoperability-vulnerabilities,下面我们看一些真实的cve漏洞案例。
2.漏洞案例
案例1:Sophos XG认证绕过 CVE-2022-1040
数据流
Sophos XG Firewall各组件调用关系可以简化如下
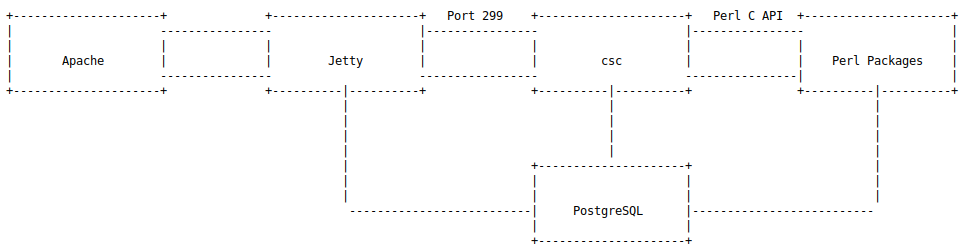
apache接受用户的http请求后转发给jetty处理过滤后,通过类似于 HTTP 的 TCP 和 UDP 协议转发给csc服务,csc处理系统的核心业务,它的核心部分是用C语言编写的,逻辑部分是通过Perl C语言接口(Perl C Language Interface)用Perl语言编写的。
核心方法分析
具体的漏洞细节分析这里不做过多描述,参考 https://blog.viettelcybersecurity.com/cve-2022-1040-sophos-xg-firewall-authentication-bypass/
我们这里只分析下关键的绕过逻辑,看下登录绕过的poc数据包
1 | POST /webconsole/Controller HTTP/1.1 |
主要起作用的是mode和json两个参数,jetty侧会通过org.json-20090211这个库解析json参数传的json数据,通过cscClient.generateAndSendAjaxEvent发送到CSC做认证,发送前会将mode参数put到解析后的json中,如果这里返回的状态码是200或者201,则认为是登录认证通过
1 | public class WebAdminAuth { |
jetty侧的org.json-20090211这个库对于重复键会抛出异常
1 | import org.json.JSONObject; |
1 | Exception in thread "main" org.json.JSONException: Duplicate key "name" |
csc使用的json-c这个库来解析输入的数据,对于重复键,则取后面一个
1 | $ cat test.c |
1 | $ gcc test.c -o test -ljson-c |
并且当json的key中出现unicode空字符时,json-c对空字符会做截断,但org.json-json库会保留
1 | $ cat test.c |
1 | $ gcc test.c -o test -ljson-c |
这个漏洞就是利用了这两个库的解析差异特性导致的绕过,我们使用下面命令开启debug,查看poc请求时的参数变化
1 | csc custom debug |
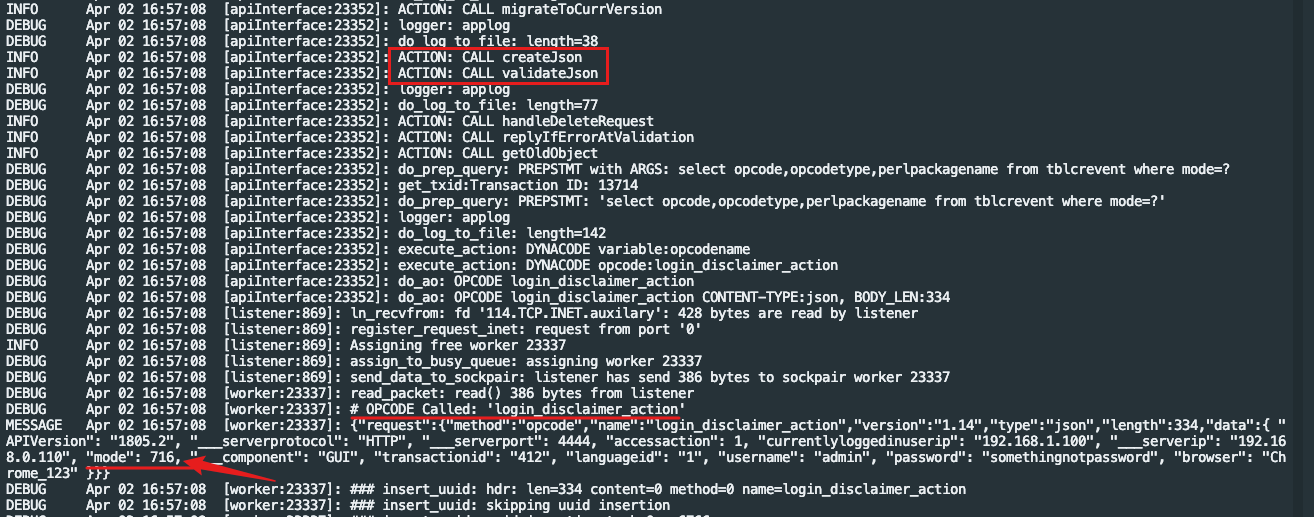
发送请poc请求,从日志可以看到,经过jetty侧org.json-json库解析转发到csc时,同时包含了mode和mode\u0000p0melo两个键

但是通过csc的createJson和validateJson方法解析后,只有原本的json数据只有一个mode键了,并且值为后一个键716,导致csc认为是请求的716模块,并且请求参数合法,导致返回了200状态码和其他符合jetty侧登录判断的数据,这就导致了登录绕过
案例2:Apache APISIX CVE-2022-25757
Apache Apisix使用了request-validation插件,它可以用来检查HTTP请求头和BODY内容,request-validation.lua中使用cjson.safe库解析字符串为json对象
1 | local _M = { |
对于重复键,cjson.safe优先取后面的键值去验证,而上游应用程序的 JSON 库选择第一个出现的值,例如 jsoniter 或 gojay 3,所以发送类似下面的json数据就能绕过数据校验,将非法数据请求到上游服务
1 | POST http://127.0.0.1:9080/10 |
这是一个典型的由于重复键优先级不一致导致的问题。
案例3: CouchDB 权限提升 CVE-2017-12635
CouchDB是一个NoSQL数据库,有点像 JSON blob的大型键值存储,具有数据验证、查询和用户身份验证功能。CouchDB通过/_users接口来管理用户账户,通过 PUT请求到 /_users/org.couchdb.user:your_username来创建或修改账户,服务器会使用 Javascript的validate_doc_update 函数检查,确保用户不会尝试让自己成为管理员。
漏洞就出在Javascript JSON 解析器(在验证脚本中使用)与 CouchDB 内部使用的名为 jiffy 的解析器(Erlang语言)之间存在差异。看下这两个解析器对相同键的处理
Erlang
1 | > jiffy:decode("{\"foo\":\"bar\", \"foo\":\"baz\"}"). |
Javascript
1 | > JSON.parse("{\"foo\":\"bar\", \"foo\": \"baz\"}") |
jiffy保留了2个重复键,用于验证的javascript取后面一个键值,并且CouchDB 数据内部表示的 getter 函数只会返回第一个值
1 | % Within couch_util:get_value |
所以我们可以通过下面的请求,让javascript解析是空,认为是非管理员用户,通过验证,而jiffy则新增的是管理员用户,从而越权新增一个admin权限用户
1 | curl -X PUT 'http://localhost:5984/_users/org.couchdb.user:oops' |
3.如何批量检测json解析器的差异性?
当我们漏洞挖掘的项目有多个json解析器的情况下,可以对https://github.com/nst/JSONTestSuite/tree/master这个工具稍作修改,就可以快速验证两个或多个解析器存在的差异。
3.1工具简介
如下图,run_test.py是主要的代码逻辑入口,parsers目录下是各种解析器,tests目录下是针对RFC 8259做了各种变形的json,test_transform目录是各种解析器识别容易有差异性json数据(超大数字、重复键、空字符等)。
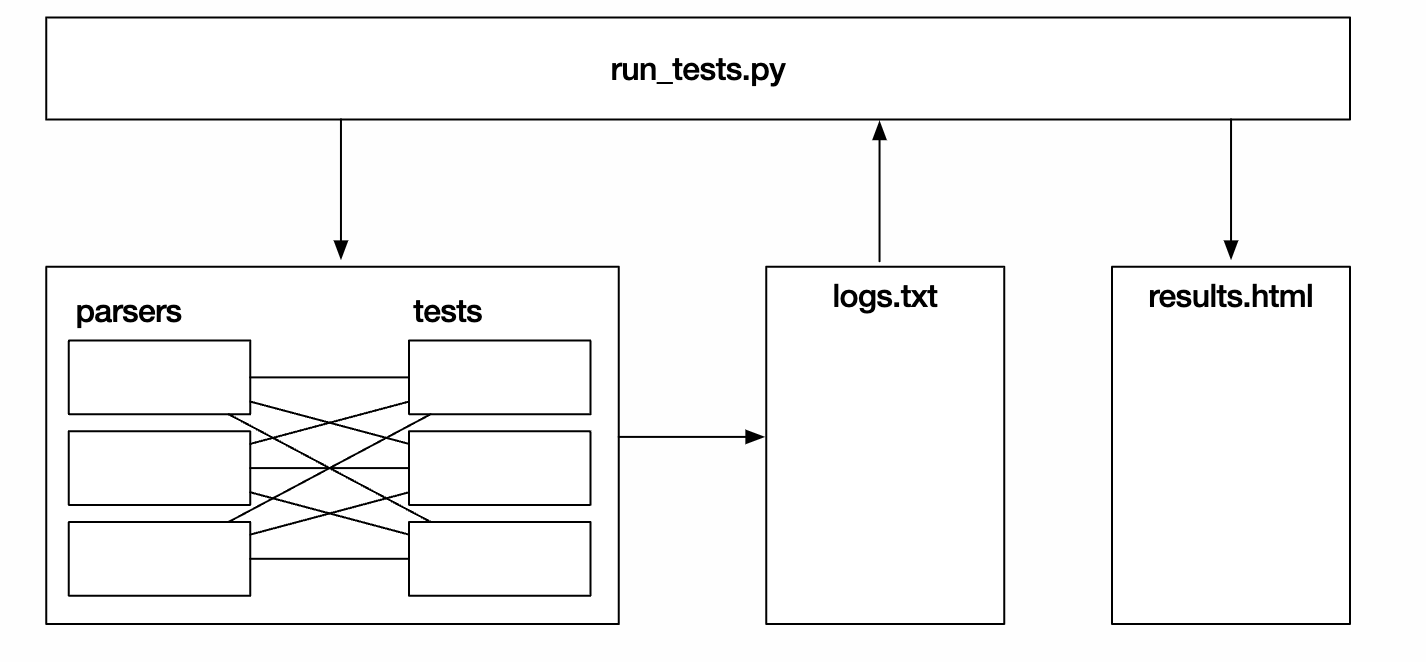
run_test.py会对parsers目录下各种解析器做一个包装,将解析器执行的命令返回状态结果记录到log.txt,然后做解析美化记录到results目录下,下面是生成的parsing.html中的对比图表,包含各种解析器对不同json数据解析后返回的状态
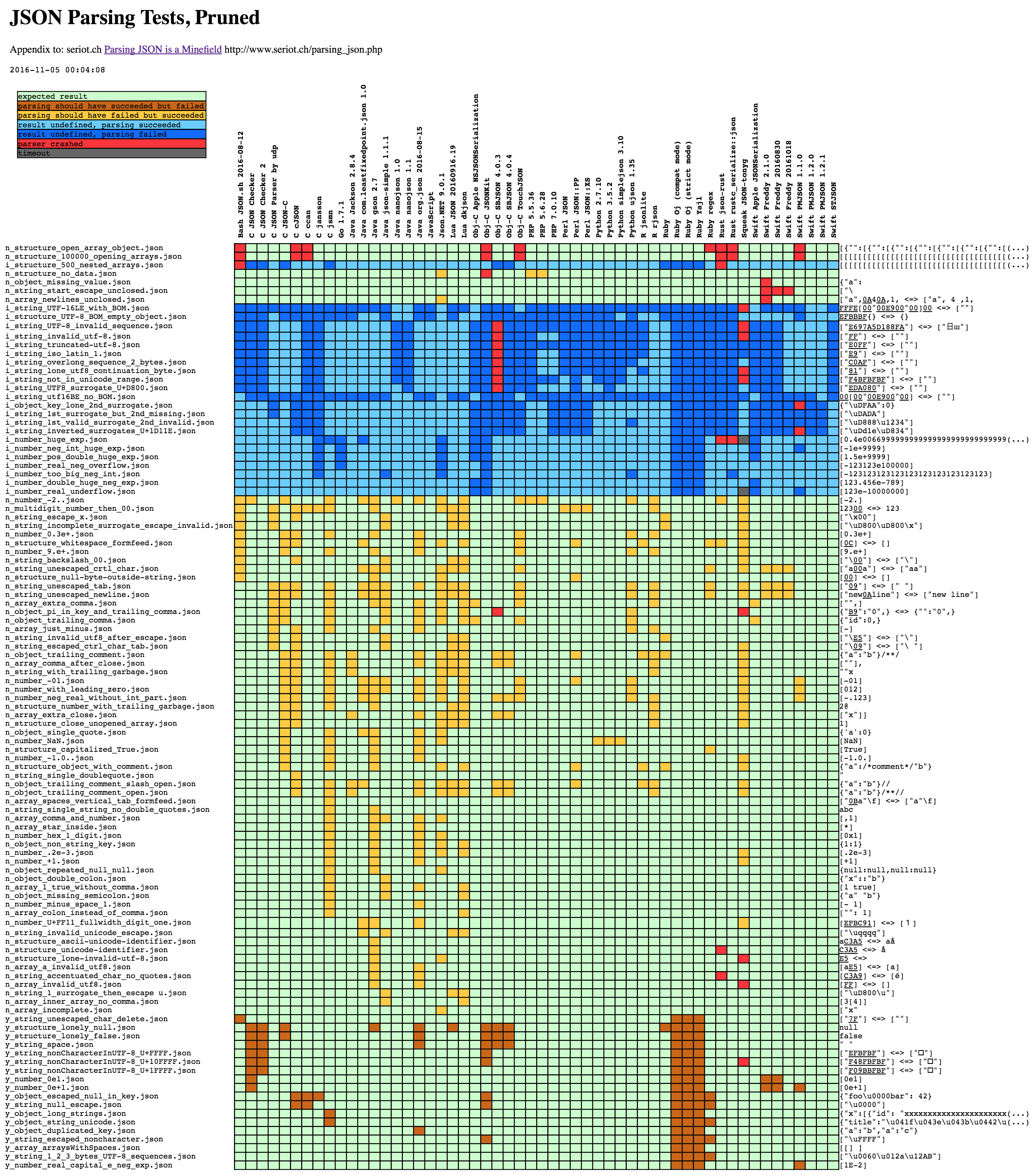
工具是针对RFC 8259标准对各json析器做的测试用例,对比的是命令执行返回状态的差异,也就是判断解析是否符合预期的成功、异常或失败。下面是run_test.py执行结果的判断
1 | if result == "CRASH": |
如果以y_开头的json用例都解析成功了,但是解析出来的内容不同,会被结果解析忽略,导致报告不会输出这种用例的结果。
所以对于解析器的差异性识别,除了解析结果的状态,我们也在意解析后的内容,所以对run_test.py调用解析器部分稍作修改,以便对比解析后的内容,下面是原来代码调用解析器部分
1 | def run_tests(restrict_to_path=None, restrict_to_program=None): |
不考虑将运行结果美化,将上面代码部分替换为如下简化代码,获取解析结果并直接输出
1 | def run_tests(restrict_to_path=None, restrict_to_program=None): |
3.2工具实践(CVE-2022-1040)
现在我们通过前文的CVE-2022-1040为例,来看如何通过这个工具来批量比较org.json-20090211和json-c这两个json解析器的差异性。
在parsers目录中只有2016版本的org.json包,所以我们需要自己去下载org.json-20090211版本的jar包,并参考TestJSONParsing.java写一个主函数调用jar去解析,然后打一个jar包供run_tests.py调用
1 | java -cp ".:json-20090211.jar" TestJSONParsing |
将TestJSONParsing.jar放在parsers下的子目录下,子目录假设以test_java_org_json_2009_02,则对应在run_tests.py的programs数组中新增一个解析器
1 | "Java org.json 2009-02-11": |
parsers目录本身已有了json-c解析器,但是格式是Mach-O的,如果想要在正常的其他架构下运行需要自己下载对应的版本并编译,将编译后的二进制文件移动到parsers/test_json-c/bin目录下并重命名为test_json-c(与run_tests.py的programs数组中的对应)
并通过filter参数限制我需要比较的2个解析器,效果如下
1 | $ cat my_parses.json |
通过上面的重复键解析结果可以看到,json-c解析器能获取重复键的最后一个,而org.json则异常了,并且对于nul的key解析也有差异。
除了这2个差异之外,还可以看到很多其他的差异,例如带注释的json数据{"a":"b"}/**/
1 | C JSON-C 解析失败 n_object_trailing_comment.json |
超大数字解析 {9999E9999:1}
1 | C JSON-C 解析失败 n_object_non_string_key_but_huge_number_instead.json |
这里只是简单的做一个解析后内容的输出,如果当json用例非常多时,有差异的结果就比较难找,读者可参考项目的结果美化逻辑,对结果做进一步的美化,方便对比。
4.总结
本文介绍了导致json解析差异性的背景,结合3个经典由json解析差异性导致的cve进行分析,并通过修改已有工具和集成新的解析器实现批量的json差异性检测。
5.参考
https://seriot.ch/projects/parsing_json.html
https://bishopfox.com/blog/json-interoperability-vulnerabilities
https://github.com/nst/JSONTestSuite/tree/master
- Post title:JSON解析不一致性漏洞探究
- Post author:p0melo
- Create time:2024-05-07 11:46:59
- Post link:2024/05/07/JSON解析不一致性漏洞探究/
- Copyright Notice:All articles in this blog are licensed under BY-NC-SA unless stating additionally.